Welcome back to our in-depth exploration of APEX Block Storage for AWS. In the first part of our series, we delved into the nuances of APEX Block Storage as a viable option for database workloads and its interplay with various AWS volume types. Our discussion revealed the intricate details of performance, manageability, and cost implications, setting a solid foundation for a more targeted inquiry.
Now, in this second installment, we pivot our focus to a pivotal question that’s been simmering in the minds of many IT professionals: “Is APEX Block Storage for AWS a good candidate to replace an Amazon RDS service? or existing DB’s built upon various AWS Volume Types
This query is not just about comparing two technologies; it’s about understanding their roles in the evolving cloud infrastructure landscape and how they align with organizational needs and strategies.
As we embark on this exploration, it’s important to remember that technology choices are seldom black and white. Each option comes with its unique set of strengths, weaknesses, and use cases. Amazon RDS, a seasoned player in the cloud database service arena, offers ease of use, automation, and scalability. But so does APEX Block Storage, with its compelling features and recent advancements, present a strong case for replacement or coexistence?
So, whether you’re a cloud architect, a database administrator, or a CIO making pivotal infrastructure decisions, join us as we unravel the complexities of APEX Block Storage and Amazon RDS, and guide you towards making informed, strategic choices in your cloud journey.
Finally, lets talk about Databases
Remember the original questions?
- Why consider APEX Block Storage for AWS over a Native EBS Volume mapped to a DB VM
- Is APEX Block Storage for AWS a good candidate to replace an Amazon RDS service ?
I believe we have explored, highlighted some key challenges and differences of cloud native vs APEX Block Storage and worked a conceptual tco to address question 1, however let’s explore question 2.
Amazon RDS (indeed all AWS Database services) is a fully managed database service, meaning AWS handles the maintenance, backups, patching, scaling, and high availability of the database. In contrast, using APEX Block Storage with AWS would typically involve setting up and managing your own database on EC2 instances.

For managed services, AWS abstracts and manages the storage layer, often using EBS technology behind the scenes, but without direct user interaction or management of the EBS volumes.
Self-Managed Databases on EC2 Instances:

If you opt to manage your database yourself rather than using a managed service like Amazon RDS, you can install and run any database software on an EC2 instance. In this case, you can use EBS volumes as the storage backend for your database. This approach gives you the flexibility to use a wide range of database software that might not be available as a managed service on AWS. This is exactly that you can also do with APEX Block Storage for Public Cloud (if you so wish) i.e. map an APEX Block Storage device instead of a native EBS volume
Concerns about data mobility, protection, and replication are valid when using AWS database services. Here are some strategies and AWS features that can help address these concerns:
Data Protection
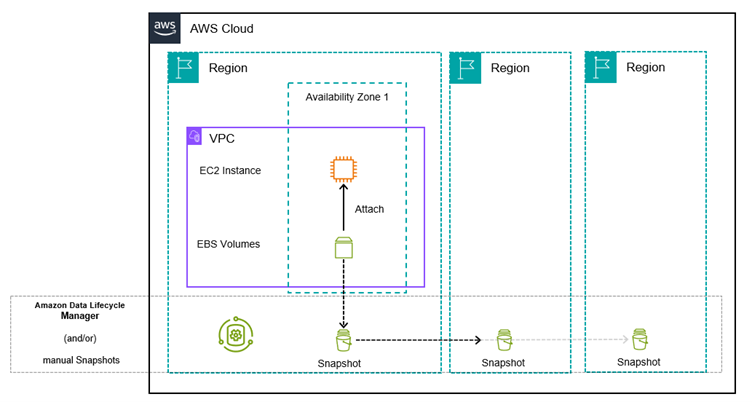
- Automated Backups: AWS services like RDS provide automated backups, which create a full backup of your database daily and store transaction logs. This allows you to restore to any point in time within your retention period.
- Snapshots: You can create manual snapshots of your databases at any time. These snapshots are stored in Amazon S3 and are highly durable. They can be used to restore databases or to create new instances.
Data Replication
- Read Replicas: Services like Amazon RDS allow you to create one or more read replicas of your database instance in the same or different AWS Regions. This not only helps in scaling read operations but also serves as a backup in case of regional failures (we’ll get to more on this later)
- Cross-Region Replication: Amazon RDS and DynamoDB offer cross-region replication, allowing you to maintain copies of your data in different geographical locations. This is crucial for disaster recovery and ensuring high availability.
- Database Migration Service (DMS): AWS DMS helps you migrate databases to AWS quickly and securely. It also supports continuous data replication with minimal downtime.
Data Mobility and Portability
- Export/Import Data: AWS provides tools and services (like AWS Data Pipeline, S3, and AWS Glue) to export and import data to and from their database services. This can be used for data mobility purposes.
- Multi-Region Applications: By architecting applications to be multi-region, you can enhance data mobility and protection. AWS provides various services that help in designing such distributed applications.
- Open Formats and Standards: When possible, using open data formats and standards for your data can aid in portability and reduce vendor lock-in.
The cost of AWS database services, data protection, and replication features can vary significantly depending on several factors such as the scale of your deployment, the specific services you use, and how you configure them. Here are some key considerations:
- Service Tier and Scale: Higher-tier database instances with more CPU, memory, and IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) are more expensive. The cost increases with the scale and performance of the database.
- Data Transfer and Storage Costs: There are costs associated with the amount of data stored and transferred. For example, transferring data out of AWS to the internet can incur costs, as does the storage used for backups and snapshots.
- Read Replicas and Cross-Region Replication: Features like read replicas and cross-region replication add costs because they require additional database instances and potentially cross-region data transfer.
- Backup and Snapshot Retention: The longer you retain backups and snapshots, the higher the storage costs. Automated backups in RDS are free up to the size of the provisioned database, but additional manual snapshots are charged.
- Database Migration Service (DMS): While AWS DMS can be cost-effective for migrations, ongoing replication tasks can incur costs depending on the compute resources used and the amount of data change.
To manage costs effectively:
- Right-Size Your Instances: Regularly monitor and adjust the size of your instances to match your actual needs.
- Use Reserved Instances: For predictable workloads, reserved instances can offer substantial savings.
- Monitor and Optimize Data Transfer: Be aware of data transfer costs, especially when using replication across regions.
- Clean Up Old Snapshots: Regularly review and delete old snapshots that are no longer needed.
If you need to design a solution where you are focused on SCALABILITY(you need to scale the reads and decrease load on the primary instance), you should look into implementing read replicas. Amazon RDS can support up to 5 read replicas per database instance (for MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle and SQL Server). If you need to implement a design where AVAILABILITY is the main concern, you should consider using a Multi-AZ deployment.
You can use Read Replicas with Multi-AZ as part of a DISASTER RECOVERY(DR) strategy for your production databases. A well-designed and tested DR plan is critical for maintaining business continuity after a disaster. A Read Replica in a different region than the source database can be used as a standby database and promoted to become the new production database in case of a regional disruption.
Or…. Look to leverage APEX Block Storage for Public Cloud that we have discussed !– Can APEX Block Storage for Public cloud make my life easier and simpler ? within the context of a DIY cloud native approach (with respect to database workloads), I believe so, yes. This argument goes beyond just Database workloads.
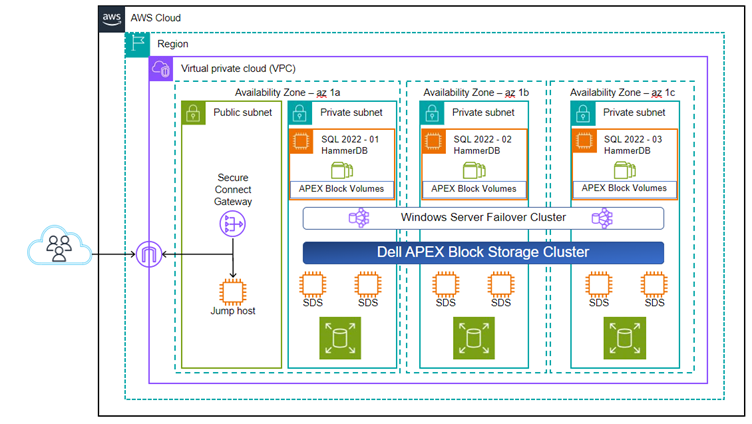
- APEX Block Storage offers high performance and scalability, more than what’s provided by standard RDS configurations. If your workload demands extremely high performance and specific tuning that RDS cannot provide, a self-managed database on EC2 with APEX Block Storage might be a better fit, negating the need for Amazon RDS read replica for example.
- Save space and utilize zero cost snaps , thin provisioning etc negating the need for AWS Snapshots while ensuring volumes do not have to be fully provisioned day 1.
APEX Navigator for Block Storage for Public Cloud can significantly aid in data mobility and data sovereignty in several ways:
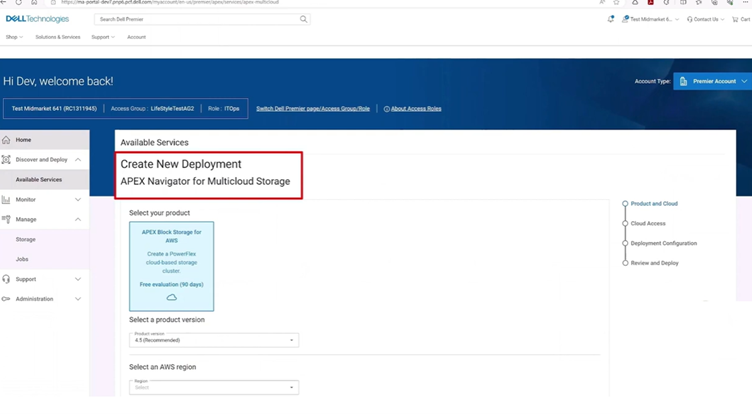
- Multicloud Data Mobility: APEX Navigator for Multicloud Storage enables seamless data mobility between on-premises environments and public cloud storage offered by Dell. This feature is particularly beneficial for organizations looking to transition to the cloud or those adopting a hybrid cloud strategy, as it allows for easy and efficient movement of data across different environments (think database volumes)
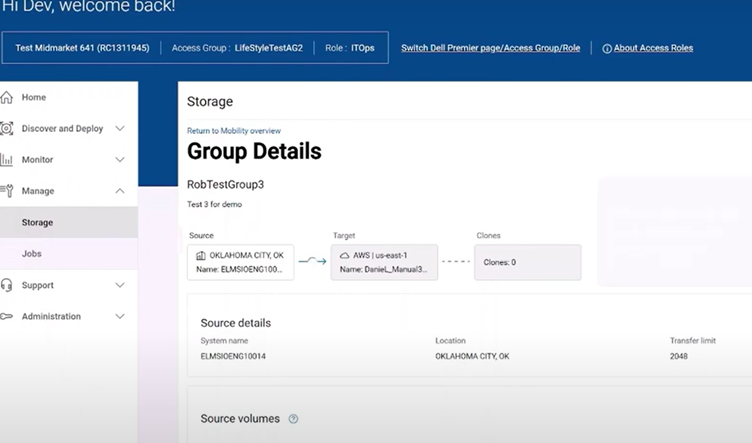
- Centralized Management Across Public Clouds: It provides a centralized management platform for Dell storage software across multiple public clouds. This SaaS tool not only simplifies the deployment, configuration, and management of storage in public clouds but also facilitates the monitoring and movement of data between on-premises and cloud environments. This centralized approach makes it easier to handle complex storage architectures and ensures consistent management practices across various clouds.
- Simplified Data Mobility and Storage Management: The APEX Navigator software is designed to simplify data mobility, storage, and container management across multicloud environments. By streamlining these processes, it reduces the complexity typically associated with managing storage (again think database volumes) and data across different cloud platforms. This simplification is crucial for businesses looking to leverage multicloud strategies without the usual operational overhead.
I believe this is a big differentiator over all the extra services you with need to leverage using a cloud native approach.
——
Dell APEX Block Storage for Public Cloud also support replication of volumes and snapshots. This functionality is crucial for data protection, disaster recovery, and ensuring high availability of your data in the cloud. Here’s how it works:
- Volume Replication: APEX Block Storage allows you to replicate storage volumes. This can be used for various purposes, such as creating redundant copies of data for disaster recovery or for maintaining data consistency across different environments.
- Snapshot Management: Snapshots are a key feature of block storage, allowing you to capture the state of a volume at a specific point in time. These snapshots can then be used for backup purposes or to create new volumes.
- Disaster Recovery: By replicating volumes and snapshots, you can prepare for disaster recovery scenarios. In the event of a failure or data corruption in your primary location, you can quickly restore data from the replicated volumes or snapshots in a different location.
- Data Mobility and Migration: Replication and snapshot capabilities also facilitate data mobility. You can easily migrate data across different environments, such as from on-premises to cloud or between different cloud regions.
- Ease of Management: These replication and snapshot features are typically integrated into the storage management interface, making it straightforward to manage these tasks without needing complex scripts or manual processes.
By leveraging these features of APEX Block Storage for Public Cloud, you can enhance your data protection strategies and ensure that your data remains safe and accessible, even in the event of system failures or other disruptions.


Leave a comment