
“Optimized thread groups, reduced lock contention, NVMe direct-write… these aren’t just buzzwords, they’re the building blocks of a storage revolution. OneFS 9.9 delivers a finely tuned engine that pushes the boundaries of performance, making it the ultimate fuel for your AI ambitions.” All of which we’ll unpack in this post.
But first… a quick re-cap as OneFS 9.9 continues on the foundations laid by previous OneFS versions (particularly OneFS 9.8), recently OneFS 9.8 marked a significant leap forward for PowerScale, particularly in the realm of high-performance computing and AI workloads. Here’s a breakdown of its key enhancements (in-case you missed it)
Performance Optimizations:
- Lock Sharding and Parallel Thread Handling: These under-the-hood improvements drastically boosted performance for streaming write-heavy workloads, essential for AI inferencing and model training. The system could scale linearly with increased compute resources, keeping GPUs busy and supporting both small and large AI/ML workflows.
- RDMA Support over NFS 4.1: This allowed for substantially higher throughput, especially in single connection and read-intensive scenarios common in machine learning and generative AI model training. It also reduced CPU utilization on both the cluster and client side.
- Client-Side NFS Driver: This driver, introduced in OneFS 9.8, brought advanced features like multipathing (using remoteports=), modified nconnect behavior, and RDMA support for improved robustness, scalability, and performance in complex network environments.
Client side NFS Driver – (multipath Driver) introduced in OneFS 9.8

New Mount Option: Remoteports=
- Purpose: This option allows an NFS client to target multiple servers or network interface cards (NICs) simultaneously.
- Benefit: By distributing I/O (input/output) operations across multiple paths, you can achieve:
- Increased bandwidth and throughput
- Load balancing across servers or NICs
- Improved fault tolerance (if one path fails, others can take over)
- Implementation: It likely creates multiple file handles to the NFS share, one for each server/NIC combination. This avoids “lock thrashing” (contention for file locks) that might occur if a single file handle were used.
Modified nconnect=:
- Background: The nconnect option in NFS controls the number of connections to use for a mount.
- Change: The default behaviour of nconnect is modified in this driver. In the standard Linux implementation, nconnect might “collapse” connections (reduce the number of active connections) under certain circumstances. This modified driver likely prevents this collapsing behavior.
- Benefit: Maintaining the specified number of connections can ensure consistent performance and avoid bottlenecks that could arise if connections are unexpectedly reduced.
RDMA Support with both:
- RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access): This is a high-performance networking technology that allows direct memory-to-memory data transfers between systems, bypassing the operating system’s network stack.
- Integration: This driver adds RDMA support and makes it compatible with both the remoteports= option and the modified nconnect option.
- Benefits: RDMA can significantly improve NFS performance by reducing latency and CPU overhead, especially for large file transfers or high-throughput workloads.
Overall Impact:
These enhancements aim to make the NFS client driver more robust, scalable, and performant, particularly in environments with multiple servers, NICs, or high-performance networking like RDMA.
Are more detailed write up is available here and look out for future tech videos on this implementation
Overall Impact:
OneFS 9.8 was a pivotal release that positioned PowerScale as a powerful solution for modern data-intensive workloads, particularly in the rapidly growing field of AI. Its focus on performance, scalability, and cloud integration made it a compelling choice for organizations seeking to accelerate their AI initiatives.
you can read more about the technical details of OneFS9.8 here and here
OneFS 9.9: The Innovation Engine Revs Up
The need for speed in the AI era is unrelenting, and OneFS 9.9 refuses to rest on its laurels. Building upon the solid foundation of OneFS 9.8, this release takes performance to a whole new level, further solidifying PowerScale’s position as the storage powerhouse for AI workloads.
200GbE Support Introduced
The headline act of OneFS 9.9 is undoubtedly the introduction of 200GbE support for both front-end and back-end fabrics. This isn’t just an incremental upgrade; it’s a notable leap that unlocks unprecedented bandwidth and throughput for your data-hungry AI applications.
- Front-End Fabric: 200GbE connectivity between clients and the PowerScale cluster enables seamless ingestion of massive datasets, ensuring your GPUs never go hungry for information.
- Back-End Fabric: With 200GbE interconnects between storage nodes, the PowerScale cluster itself becomes a high-speed data highway, ensuring rapid communication and efficient data distribution.
Prior to this release PowerScale was limited to 100GB ether on both the front end and back end fabric, as of this release OneFS 9.9 200GbE is now supported on both the front end and back end fabric –
Support will initially be for the NVIDIA CX-6 VPI 200GbE network card. The NVIDIA CX-6 VPI 200GbE is a powerful and versatile NIC that plays a crucial role in enabling OneFS 9.9 to achieve its exceptional performance benchmarks. If you’re looking to accelerate your AI initiatives with a storage solution that can keep up with the most demanding workloads, the combination of OneFS 9.9 and the CX-6 VPI 200GbE is a formidable choice. Support for 200GbE will be available on the F710 platform.
How AI is Driving the Need for 200GbE in Storage (and beyond..)

The AI revolution isn’t just about smarter algorithms; it’s also about the massive infrastructure required to support it. Training large models, fine-tuning for specific tasks, implementing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and performing inferencing all demand immense computational power and lightning-fast data access. This is where 200GbE Ethernet is emerging as a game-changer for storage arrays.
Why 200GbE is Becoming Essential
Massive Data Movement: AI workloads often involve moving terabytes of data between storage and compute nodes. 200GbE provides the bandwidth needed to avoid bottlenecks that would cripple performance.
Parallel Processing: Training and inferencing often leverage parallel processing across multiple GPUs or specialized AI chips. This requires storage that can handle simultaneous, high-speed data requests – a task well-suited for 200GbE.
Real-time Demands: Applications like RAG, where models need to retrieve and process information on the fly, require ultra-low latency connections to storage. 200GbE’s speed helps minimize delays and deliver results in real time.
Futureproofing: AI models are growing in size and complexity. 200GbE offers a scalable solution that can adapt to the increasing demands of tomorrow’s AI workloads.
Impact on Storage Architectures
Front-End Storage: 200GbE is becoming the preferred interface for connecting servers and storage arrays. Its speed and scalability make it ideal for handling the high throughput and IOPS requirements of AI applications.
Back-End Storage: Within storage arrays, 200GbE is used to interconnect storage nodes and enable fast data transfer between them. This is crucial for maintaining performance in distributed storage systems.
Industry Trends
We’re already seeing major storage vendors embrace 200GbE, offering arrays and network adapters specifically designed for AI workloads. Cloud providers are also investing heavily in 200GbE infrastructure to support their AI offerings.
The Bottom Line
The AI market is rapidly evolving, and the infrastructure supporting it must evolve as well. 200GbE Ethernet is proving to be a critical technology for enabling the next generation of AI applications. Its speed, scalability, and low latency make it the perfect match for the demanding requirements of AI workloads.
The Future: A Glimpse Beyond 200GbE
OneFS 9.9 is not the end of the road (Believe me were just getting started!). The OneFS file system’s inherent scalability and Dell’s commitment to innovation point towards a future where 400GbE and even 800GbE speeds could become a reality. PowerScale is ready to embrace the next generation of networking technologies, ensuring your AI infrastructure remains ahead of the curve.
The OneFS 9.9 File System: Built for Speed
The OneFS file system, the heart and soul of PowerScale, is inherently designed to handle the extreme demands of AI workloads. Its ability to scale linearly with increased compute resources and its robust architecture make it the ideal platform for harnessing the full power of 200GbE.
Software Enhancements
- Protocol Stack Optimization:
- Reduced thread lock contention: By distributing work across thread groups in a round-robin fashion, OneFS minimizes situations where multiple threads are waiting for the same resource, improving overall parallelism.
- Optimized thread group count: The number of thread groups is now dynamically adjusted based on the number of CPU cores available. This ensures that systems with more cores can take full advantage of increased parallelism.
- Locking Mechanisms:
- Reduced contention on turnstile locks: Turnstile locks are a type of lock used in the file system. By increasing the number of retries before a thread gives up on acquiring a lock, OneFS 9.9 allows locks to spin for a bit longer, potentially avoiding more costly context switches.
- Focus on NUMA nodes: Turnstile lock contention is particularly problematic on systems with Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) architectures, so this improvement specifically targets those scenarios.
- Direct-write:
- Bypass journal for new NVMe blocks: When writing to newly allocated blocks on NVMe storage nodes, OneFS 9.9 can now skip the journaling process. This avoids bottlenecks caused by journal flush operations, especially on the listed storage node models (F600p, F900, F710, F910).
Performance Benchmarks: The Proof is in the Pudding
Benchmark results show significant performance improvements across various workloads:
Let’s talk about the importance of reads – fast streaming reads are important for AI training and fine-tuning because they help sustain high throughput. In these processes, large amounts of data need to be accessed and processed quickly. Fast streaming reads ensure the GPU doesn’t have to wait for data, allowing it to operate at peak efficiency. This can significantly reduce the overall training time and improve the quality of the resulting models.
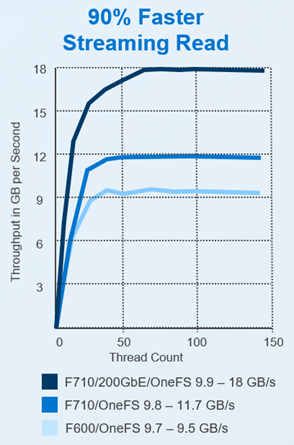
Read Throughput: OneFS version 9.9 delivers higher throughput in GB/s compared to older versions across all thread counts. This is particularly notable in the F710 with 200GbE configuration, where it achieves 18 GB/s throughput with OneFS 9.9 compared to 11.7 GB/s with OneFS 9.8. This increase in bandwidth enables GPUs to sustain high utilization rates, allows for faster training times, and improves the quality of AI models by supporting the use of larger datasets and more complex model architectures.
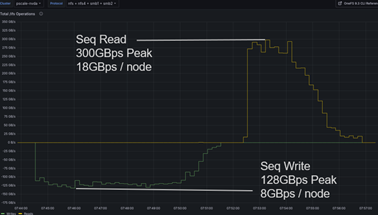
Sequential Read: Lets look at the remarkable sequential read performance of a 16-node PowerScale F710 cluster running OneFS 9.9. It achieves a peak throughput of 300 GB/s (gigabytes per second), again, translating to 18 GB/s per node. This showcases the system’s ability to quickly deliver massive amounts of data, crucial for AI models that need to access training data rapidly.
And what about writes?
While reads are essential for providing the data for AI models, fast writes are equally important for saving model checkpoints, weights, and ensuring efficient communication in distributed training environments. Both fast reads and writes contribute to a faster and more efficient AI training and fine-tuning process.
- Checkpoints: During the training process, checkpoints are saved periodically. These checkpoints are snapshots of the model’s current state and allow training to be resumed from that point in case of interruptions or failures. Fast writes ensure these checkpoints are saved quickly, minimizing downtime.
- Model Weights: The final weights of a trained model, or intermediate weights during fine-tuning, need to be saved to storage. These files can be quite large, and slow writes can bottleneck the entire training process. Fast writes allow for quick saving of these weights, improving overall efficiency.
- Distributed Training: In scenarios where AI training is distributed across multiple nodes or GPUs, fast writes become even more critical. Models need to synchronize their weights across nodes regularly, and slow writes can cause significant delays in this process.
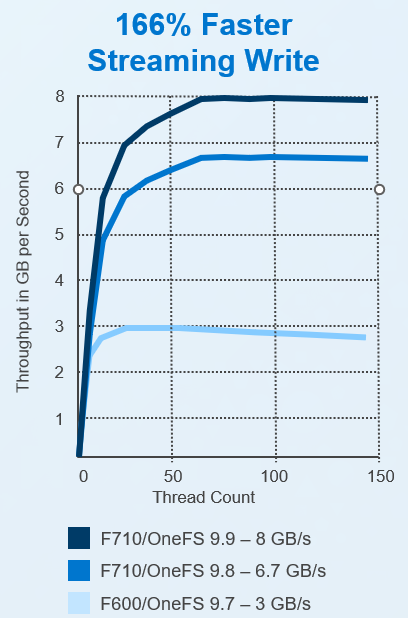
OneFS version 9.9 delivers higher throughput in GB/s compared to older versions across all thread counts. This is particularly notable in the F710 with 200GbE configuration, where it achieves 18 GB/s throughput with OneFS 9.9 compared to 11.7 GB/s with OneFS 9.8. This increase in bandwidth enables GPUs to sustain high utilization rates, allows for faster training times, and improves the quality of AI models by supporting the use of larger datasets and more complex model architectures.
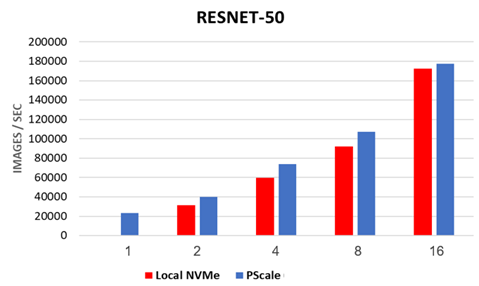
PowerScale now matches performance & scale of local NVMe storage on real AI workloads
lets quickly talk about ResNet-50: This is a well-known convolutional neural network architecture commonly used in image recognition tasks. The graph shows that PowerScale’s performance on ResNet-50 training, using up to 16 systems with 8-way GPUs, is comparable to that of local NVMe storage. This is a significant achievement, as it demonstrates that PowerScale can provide the high-speed storage required for AI without sacrificing the benefits of centralized, scalable storage.
The bar graph below illustrates how PowerScale, using the OneFS 9.9 file system, can match the performance and scalability of local NVMe storage, which is typically known for its speed, in real AI workloads.
PowerScale with OneFS 9.9 meeting NVIDIA SuperPOD “Best” spec while utilizing 40% less Rack Space
NVIDIA SuperPod is a reference architecture for building large-scale AI infrastructure. It combines NVIDIA’s cutting-edge GPUs with high-performance networking and storage components to create a powerful and scalable platform for AI research and development.
PowerScale’s certification for NVIDIA SuperPod signifies that it has met rigorous testing standards for compatibility, performance, and reliability within the SuperPod ecosystem. This means that organizations building AI infrastructure based on SuperPod can confidently choose PowerScale as their storage solution, knowing that it has been validated to deliver optimal results.
What Does SuperPod Certification Entail?
- Compatibility Testing: PowerScale undergoes extensive testing to ensure seamless integration with NVIDIA’s GPUs, networking equipment, and software stack.
- Performance Benchmarking: Rigorous benchmarks are conducted to verify that PowerScale can deliver the throughput, IOPS, and latency required by demanding AI workloads within the SuperPod environment.
- Reliability Testing: PowerScale is subjected to stress tests and failure scenarios to ensure that it can maintain data integrity and availability even under extreme conditions.
You can read more about the announcement here
As AI workloads continue to evolve and grow in complexity, PowerScale stands ready to meet the challenge. With a future that promises even greater speeds and capabilities, Dell Technologies has once again proven its commitment to innovation and its dedication to this product.


Leave a reply to PowerScale OneFS 9.9: Enhanced Performance with CoS/QoS Tagging Cancel reply